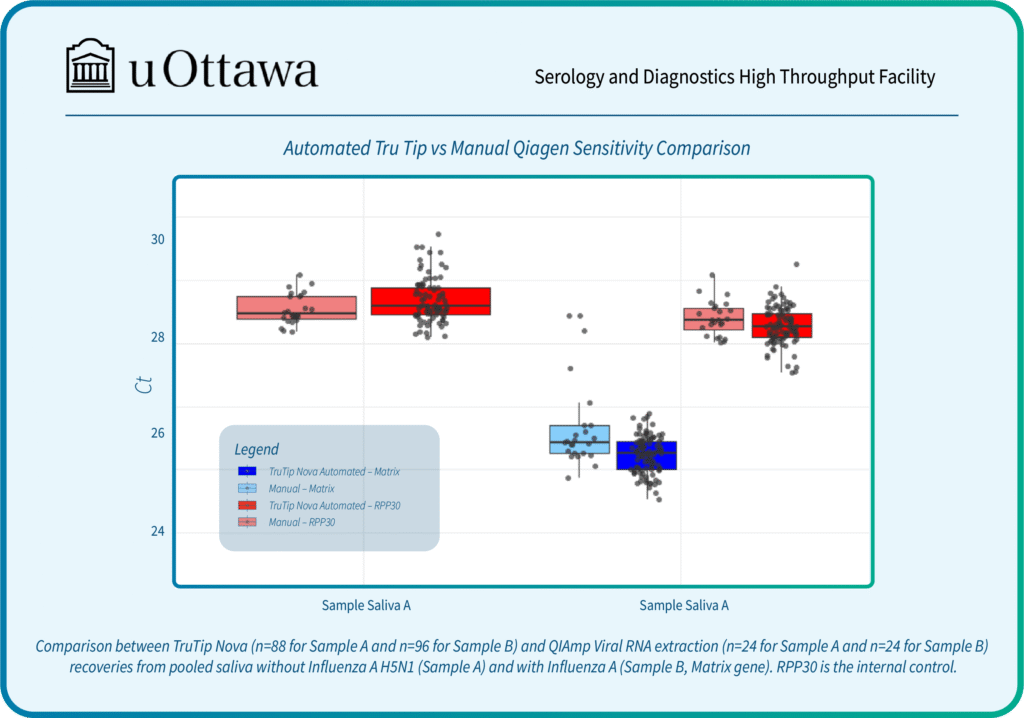
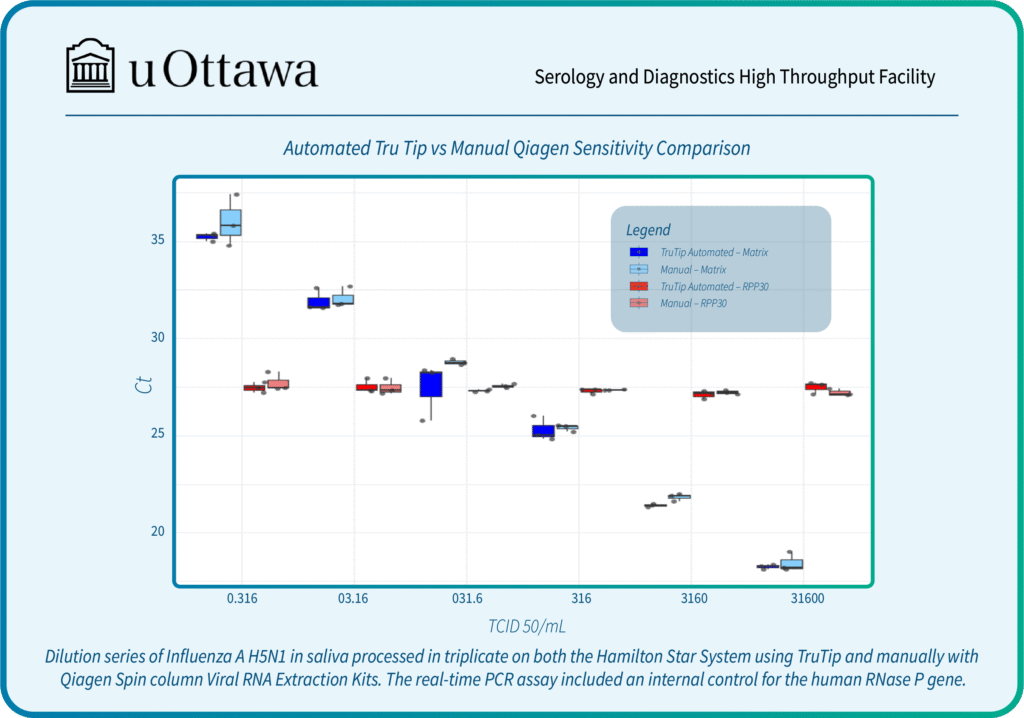
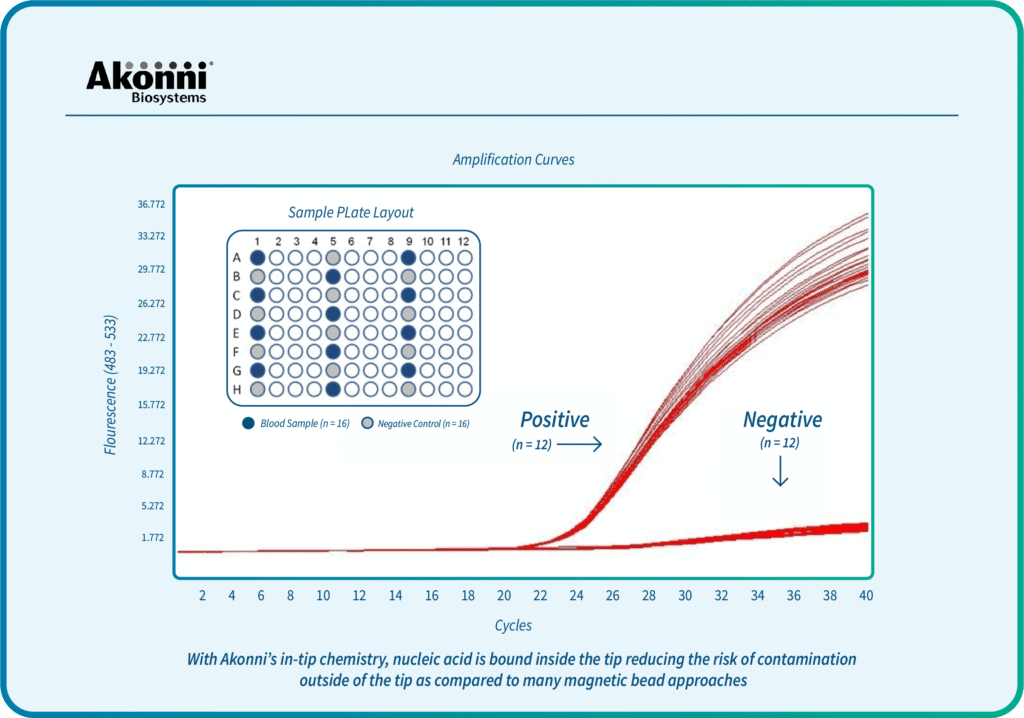
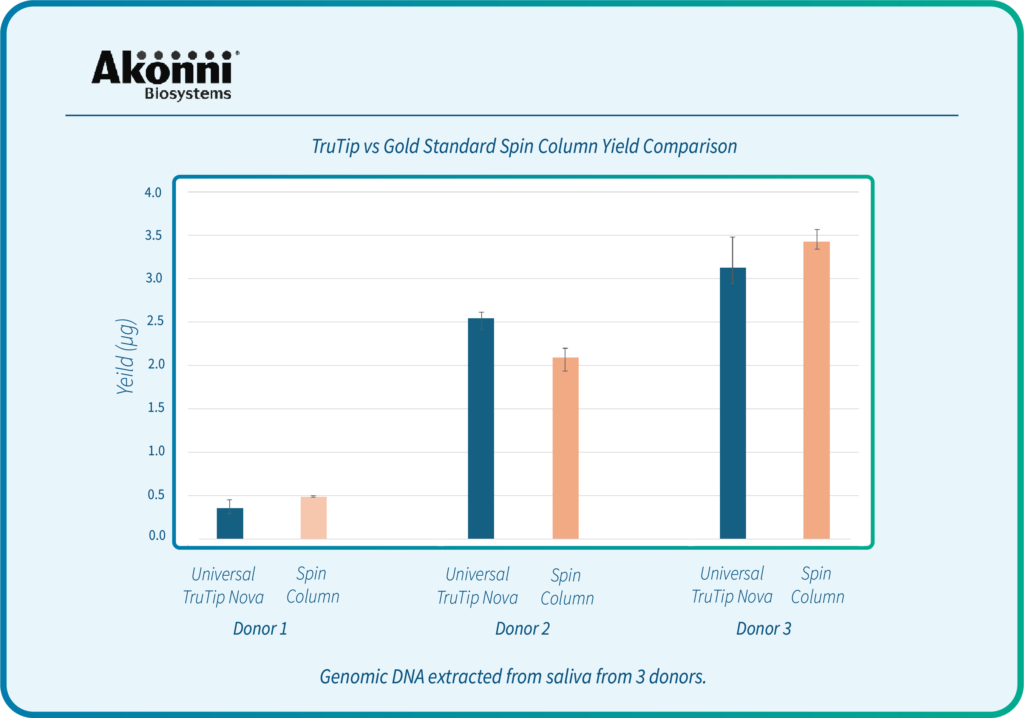
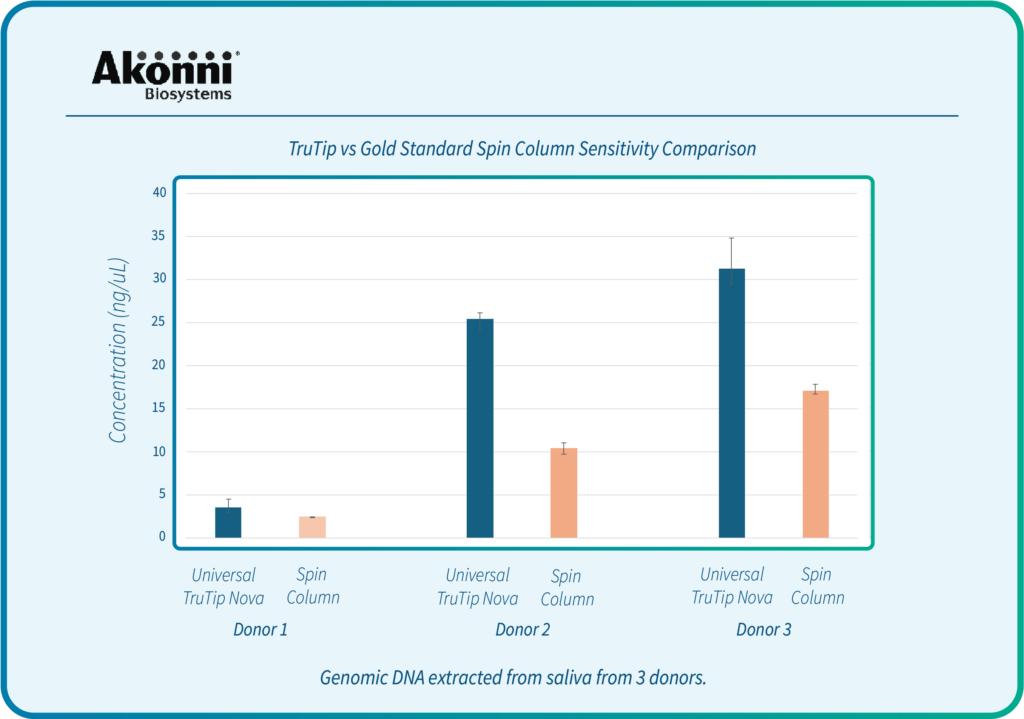
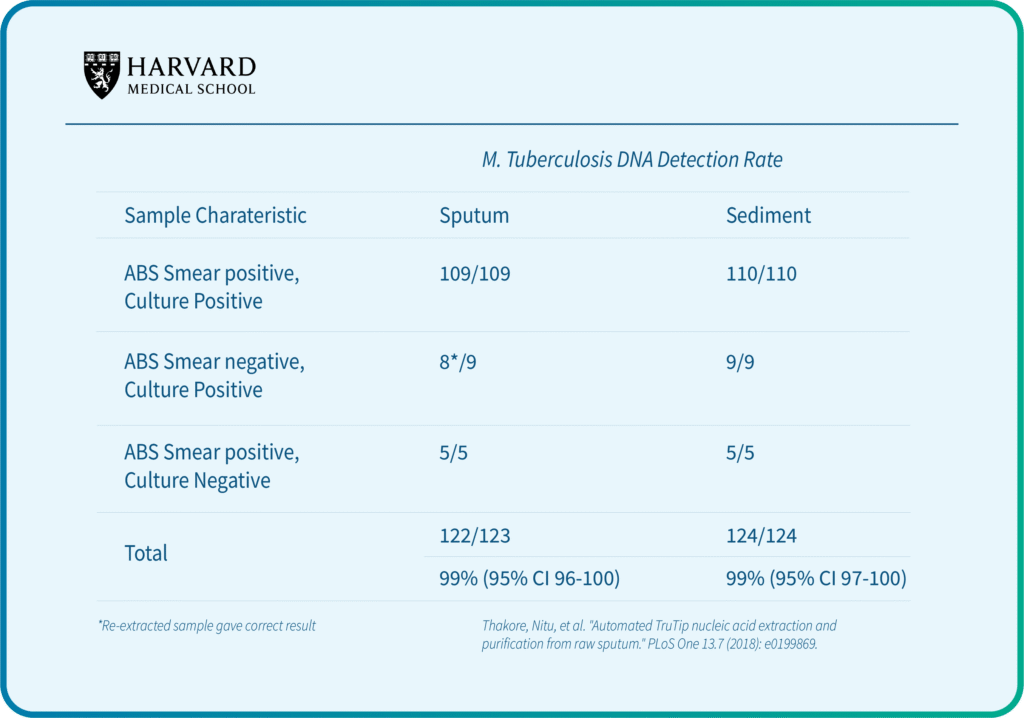
Syed, R.R., Catanzaro, D.G., Colman, R.E., Cooney, C.G., Linger, Y., Kukhtin, A.V., Holmberg, R.C., Norville, R., Crudu, V., Ciobanu, N. and Codreanu, A., 2023. Clinical evaluation of the XDR-LFC assay for the molecular detection of isoniazid, rifampin, fluoroquinolone, kanamycin, capreomycin, and amikacin drug resistance in a prospective cohort. Journal of clinical microbiology, 61(3), pp.e01478-22.
PMID: 36757183
Mesman, A.W., Soto, M., Coit, J., Calderon, R., Aliaga, J., Pollock, N.R., Mendoza, M., Mestanza, F.M., Mendoza, C.J., Murray, M.B. and Lecca, L., 2019. Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in pediatric stool samples using TruTip technology. BMC Infectious Diseases, 19(1), p.563. PMCID: PMC6598370
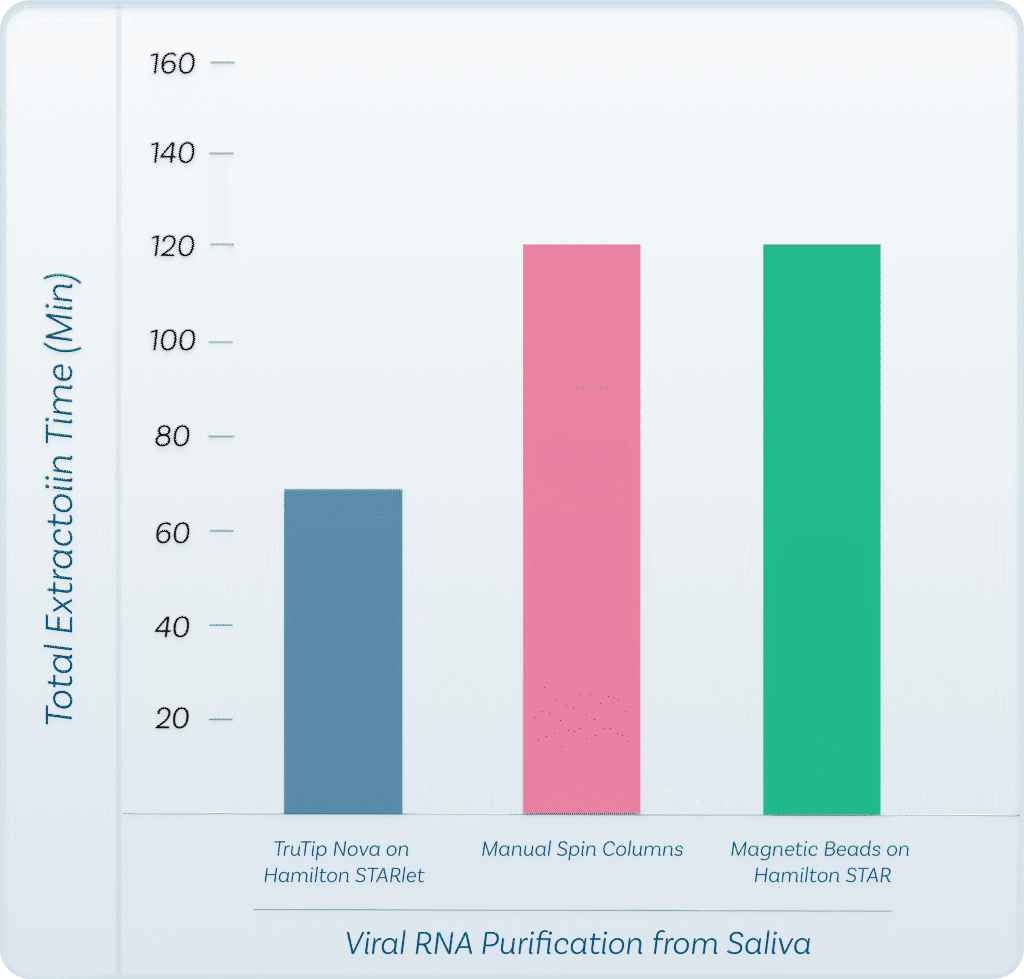
Thakore, N., Norville, R., Franke, M., Calderon, R., Lecca, L., Villanueva, M., Murray, M.B., Cooney, C.G., Chandler, D.P. and Holmberg, R.C., 2018. Automated TruTip nucleic acid extraction and purification from raw sputum. PloS one, 13(7), p.e0199869. PMCID: PMC6033430
Thakore, N., Garber, S., Bueno, A., Qu, P., Norville, R., Villanueva, M., Chandler, D.P., Holmberg, R. and Cooney, C.G., 2018. A bench-top automated workstation for nucleic acid isolation from clinical sample types. Journal of microbiological methods, 148, pp.174-180. PMCID: PMC5944857